Bacterial endocarditis: an overview of the pathophysiology, symptoms and treatment
To enhance your knowledge of bacterial endocarditis, including its pathophysiology and causes
To familiarise yourself with the signs and symptoms of bacterial endocarditis
To understand what is involved in the treatment and management of bacterial endocarditis
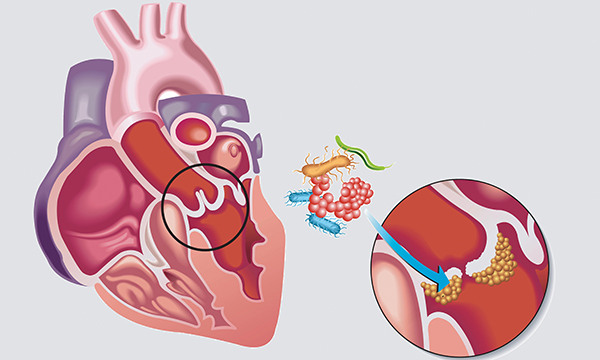
Infective endocarditis is a serious and potentially life-threatening cardiac infection which affects the endocardial (inner) layer of the heart and primarily involves the heart valves. It is most often caused by a bacterial infection, with Gram-positive streptococci, staphylococci and enterococci being the most common pathogens. Where the condition is known to have been caused by bacteria, it is referred to as bacterial endocarditis. While it is still a relatively rare condition, the numbers of infective endocarditis cases and associated mortality have increased over the past 30 years, making it a global public health concern. This article provides an overview of the anatomy and pathophysiology, epidemiology, aetiology, diagnostic criteria, clinical presentation, treatment and management of bacterial endocarditis. The article focuses on bacterial endocarditis but uses the term infective endocarditis when discussing the condition in general.